Project's News

The EHAWEDRY technological system
How to overcome the feasibility limitation of thermoelectric device The EHAWEDRY technological system revolutionises the waste heat recovery processes by using electrochemical capacitors. Expensive materials and extremely low-efficient energy conversion processes, based on mechanical components such as expanders, compressors and turbines, limit the market scalability of thermoelectric devices, especially for low-medium grade heat. EHAWEDRY, a…

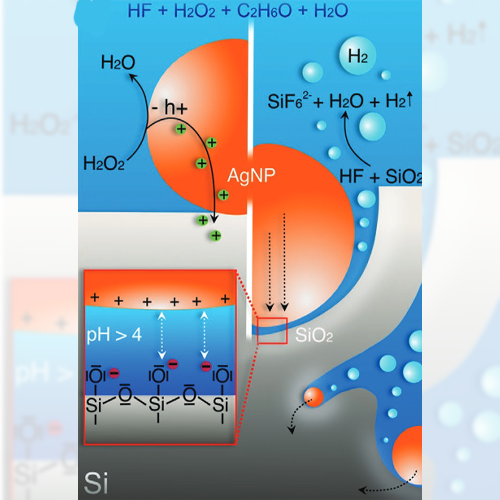
Porous Silicon Wafer
Wafer-Scale Fabrication of Hierarchically Porous Silicon and Silica by Active Nanoparticle-Assisted Chemical Etching and Pseudomorphic Thermal Oxidation Abstract Many biological materials exhibit a multiscale porosity with small, mostly nanoscale pores as well as large, macroscopic capillaries to simultaneously achieve optimized mass transport capabilities and lightweight structures with large inner surfaces. Realizing such a hierarchical…
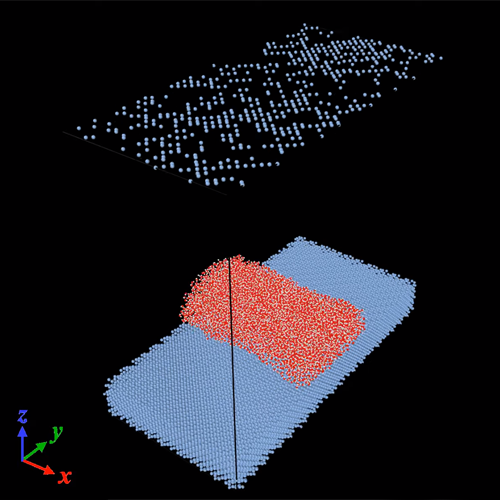
Hybrid Muscle Mechanics
How nanoporous silicon-polypyrene hybrids flex their muscles in aqueous electrolytes: In operando high-resolution x-ray diffraction and electron tomography-based micromechanical computer simulations Abstract Macroscopic strain experiments have revealed that silicon crystals traversed by parallel, channel-like nanopores functionalized with the artificial muscle polymer polypyrrole (PPy) exhibit large and reversible electrochemomechanical actuation in aqueous electrolytes. On a…
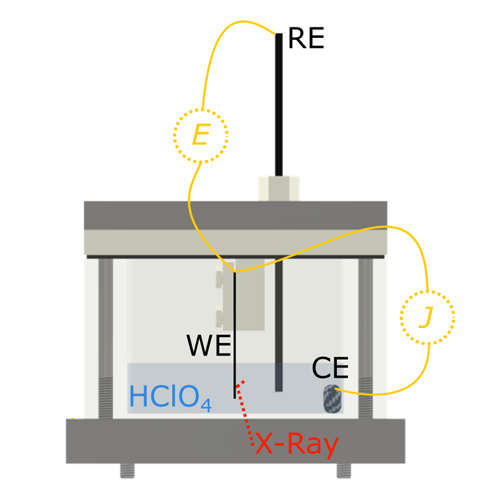
Contact Angle Simulations
Molecular dynamics simulation of receding and advanced contact angle dynamics Sergii Burian and Volodymyr Kovalchuk, Institute of biocolloid chemistry named after F.D. Ovcharenko of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. These results are a part of studies performed under the European Commission project “EHAWEDRY” within the scope of FP Horizon 2020 (Grant Agreement No. 964524)…
Liquid Meniscus Flow
Adsorption layer and flow within liquid meniscus in forced dewetting In surfactant solutions, the bulk hydrodynamic flow couples to extensional/compressional surface flows due to Marangoni stresses induced at the interface. With the increasing surfactant concentration, these Marangoni stresses can suppress the surface flows and lead to non-moving, retarded, surfaces. We review this phenomenon with…
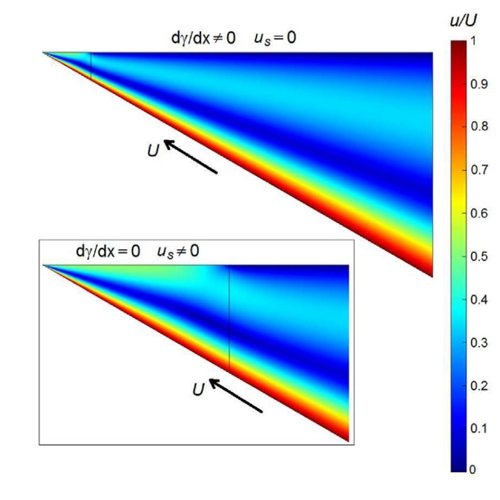
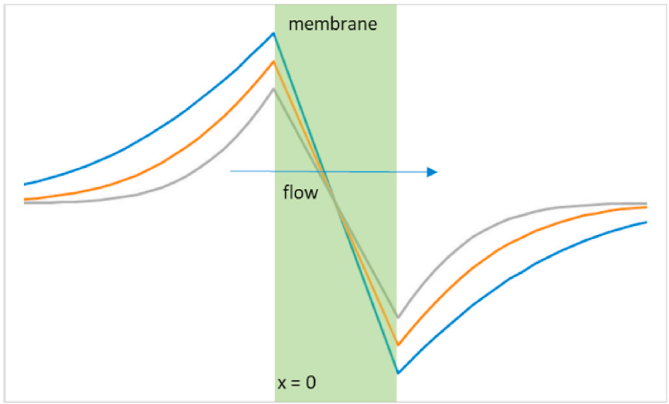
Electrolyte Flux Analysis
Kinematic and volumetric analysis of coupled transmembrane fluxes of binary electrolyte solution components. The paper deals with relationships between the individual transmembrane fluxes of binary electrolyte solution components and the experimentally measurable quantities describing rates of transfer processes, namely, the electric current, the transmembrane volume flow and the rates of concentration changes in the…
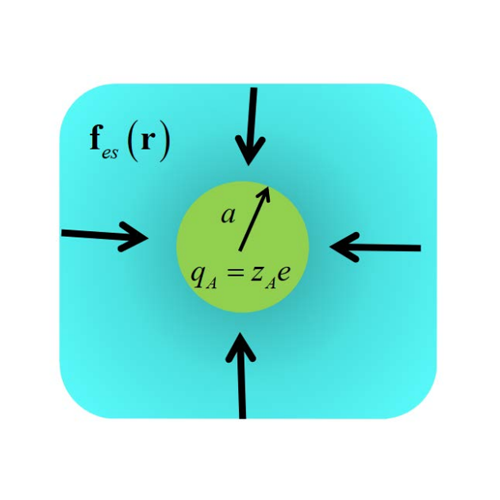
Electrokinetic Energy Conversion
Evaporation-driven electrokinetic energy conversion: Critical review, parametric analysis and perspectives Energy harvesting from evaporation has become a 'hot' topic in recent years. Researchers have speculated on several possible mechanisms, with electrokinetic energy conversion being the least hypothetical. The basics of pressure-driven electrokinetic phenomena, such as streaming current and streaming potential, have long been established.…
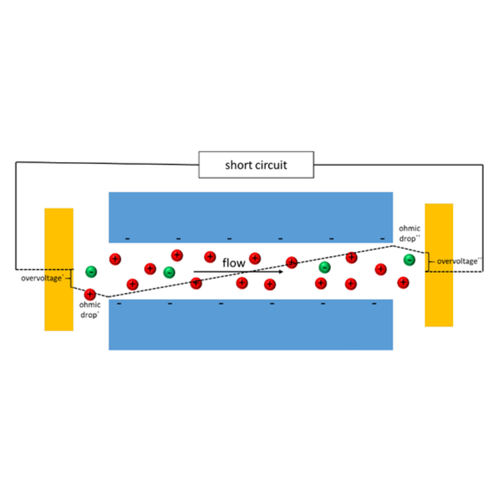
Electron-Conducting Streaming
Streaming Potential with Ideally Polarizable Electron-Conducting Substrates With nonconducting substrates, streaming potential in sufficiently broad (vs Debye screening length) capillaries is well known to be a linear function of applied pressure (and coordinate along the capillary). This study for the first time explores streaming potential with ideally polarizable electron-conducting substrates and shows it to…
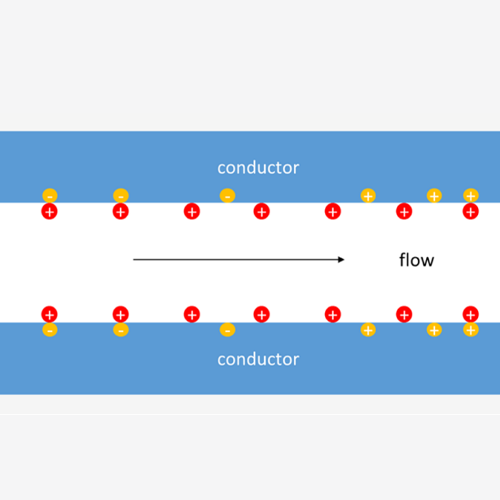
Ionic Diffusion Dynamics
Osmotic Pressure and Diffusion of Ions in Charged Nanopores. The transport of ions and water in nanopores is of interest for a number of natural and technological processes. Due to their practically identical long straight cylindrical pores, nanoporous track-etched membranes are suitable materials for investigation of its mechanisms. This communication reports on simultaneous measurements…
Nanoporous Membrane Performance
Time-resolved pressure-induced electric potential in nanoporous membranes: Measurement and mechanistic interpretation. Performance of charged nanoporous membranes in ion separations and electrokinetic energy conversion is controlled by their surface-charge density. This (or related such as zeta-potential) parameter has often been obtained from measurements of pressure-induced electric potential typically referred to as streaming potential. However, with…